Temperature Basics
Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold an object is relative to another object. This is different from heat, which is the flow of thermal energy between objects with different temperatures.
People behind temperature scales
The first sealed thermometer was constructed in 1654. Today’s standards were developed by Gabriel Fahrenheit(1717), Anders Celsius(1742), William Thomson 1st Baron Kelvin (1848). Fahrenheits scale is based on tradition of using 12 divisions, just like 1ft = 12 in. Celsius was designed with 100 divisions, also called the centigrade scale. Kelvin uses molecular energy.
Converting between Scales
Converting Kelvin and Celsius
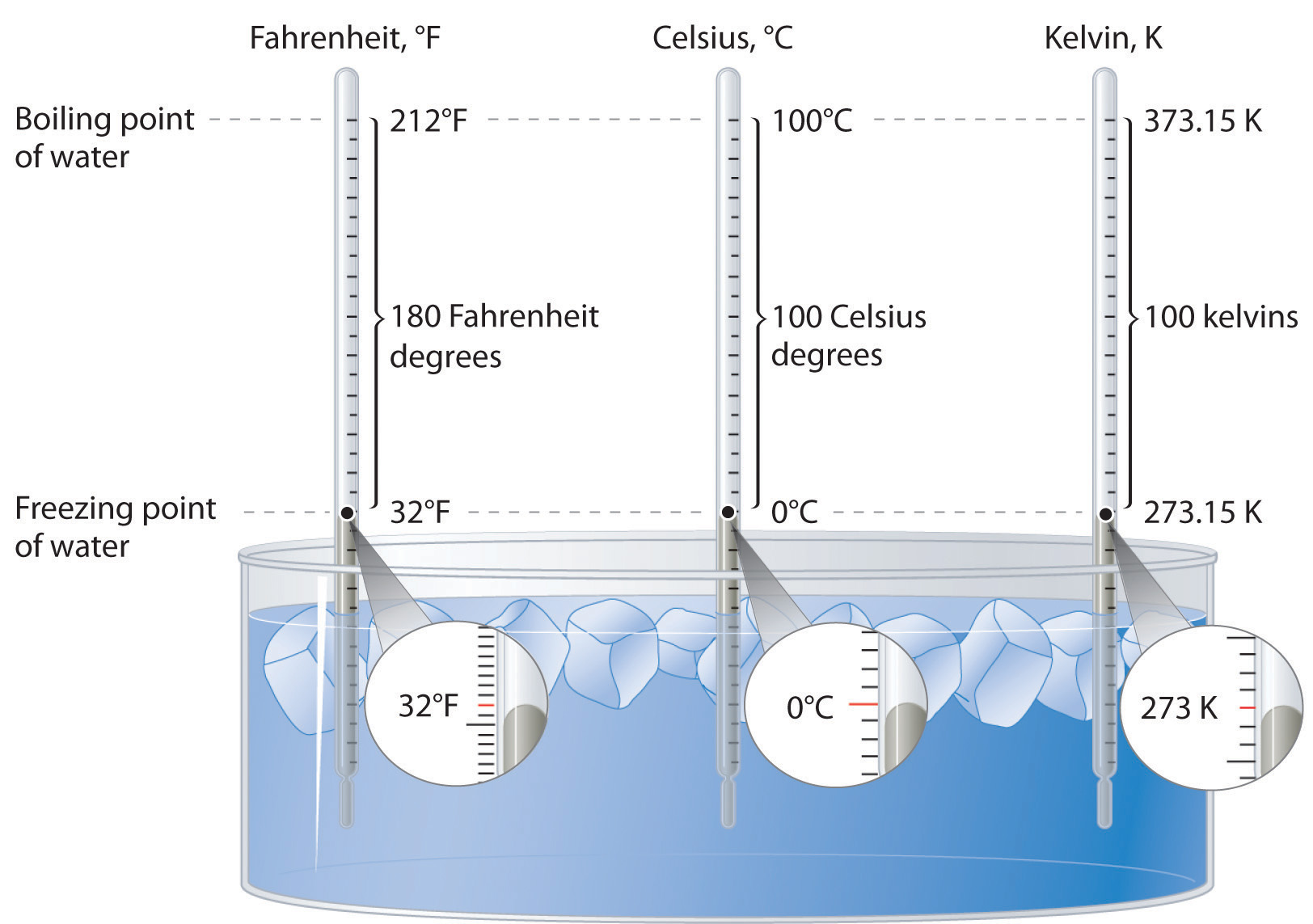
Kelvin and Celsius are easy to converty since they are the same size in degrees. Freezing point of water is 0°C = 273.15K. Boiling point of water is 100°C = 373.15 K.
T (in °C) + 273.15 = T (in K)
T (in K) − 273.15 = T (in °C)
Converting Fahrenheit and Celsius
°C = (5/9)*(°F-32)
°F = (9/5)*(°C)+32
Temp Quick reference chart
Three different scales that are commonly used to measure temperature:
| Kelvin (K) | Celsius (°C) | Fahrenheit (°F) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute zero | 0 | -273.15 | -459.67 |
| Space | 2.7 | -235 | -455 |
| Water freezes | 273.15 | 0 | 32 |
| Human Body | 310.0 ±0.7 | 36.8 ±0.7 | 98.2 ±1.3 |
| Water boils | 373.15 | 100 | 212 |
| Surface of the Sun | 5800 | 5526 | 9980 |
Space temperatures
| Range (km) | Range (ft) | Range (mi) | Temp (°F) | Temp (°C) | Temp (K) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Troposphere | 0 - 11 | 36,000 | 0 - 6.8 | 59 - (-65) | 15 - (-54) | 288 - 219 |
| Stratosphere | 11 - 51 | 167,000 | 6.8 - 31 | (-65) - 19 | (-54) - (-7) | 219 - 266 |
| Mesosphere | 51 - 71 | 232,000 | 31 - 44 | 19 - (-40) | (-7) - (-40) | 266 - 233 |
| Ionosphere | 71+ | 232,000+ | 44+ | < (-89) | < (-67) | < 206 |